Advanced Monitoring Parameters: dPmx
Contractility
Contractility is another factor that influences cardiac output. Contractility of the myocardium represents the ability of the heart to contract independent of the influence from preload or afterload. Substances that cause an increase in intracellular calcium ions lead to an increase in contractility. Different concentrations of calcium ions in the cell lead to a different degree of binding between the actin (thin) and myosin (thick) filaments of the heart muscle.
Left Ventricular Contractility (dPmx)
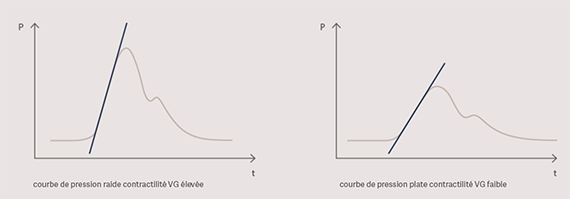
From the arterial pressure curve, the pressure changes during the systolic phase can be analysed and a measure of the pressure increase over time (analysed in speed) is calculated. The steeper the upslope of the curve, the higher the contractility of the left ventricle.
As the upslope also depends on the individual compliance of the aorta, the parameter should primarily be viewed and evaluated as part of the overall trend.[1]