Advanced Monitoring Parameters: PVPI
Pulmonary Vascular Permeability Index (PVPI)
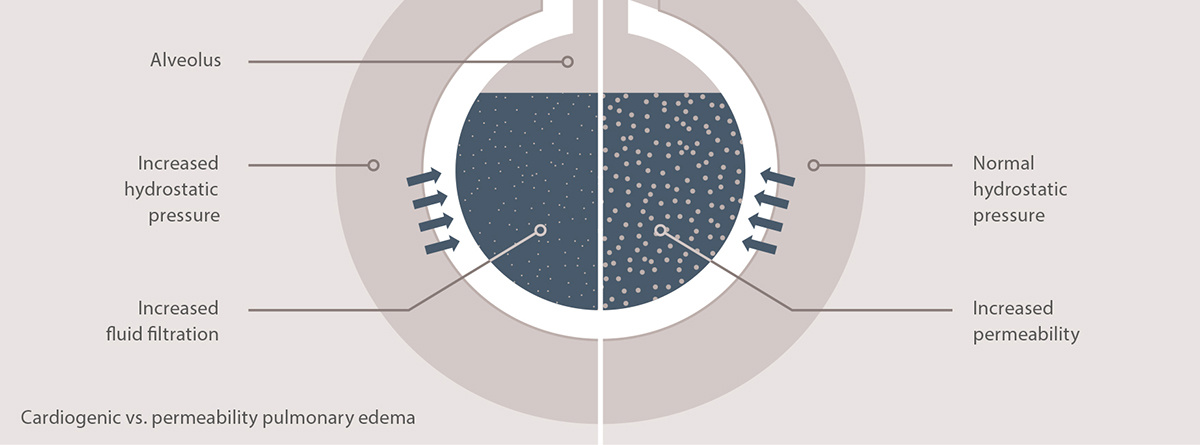
When pulmonary edema is present (measured using extravascular lung water), the next important question is: What is the reason for the pulmonary edema? In general there are two main sources of pulmonary edema.[1]
Cardiogenic pulmonary edema
Caused by intravascular fluid overload, hydrostatic pressure increases. This causes fluids to leak into the extravascular space.
Permeability pulmonary edema
Vascular permeability is increased by an inflammatory reaction caused, for example, by sepsis. This leads to the increased transfer of fluids, electrolytes and proteins from the intravascular to the extravascular space, even with a normal to low intravascular fluid status and hydrostatic pressure.