Neurally Adjusted Ventilatory Assist NAVA
Neurally Adjusted Ventilatory Assist NAVA is a mode of mechanical ventilation, where the ventilator is controlled directly by the patient’s own neural respiratory drive. The neural control of respiration originates in the respiratory center, where signals are transmitted through the phrenic nerve to create electrical activity of the diaphragm (Edi).
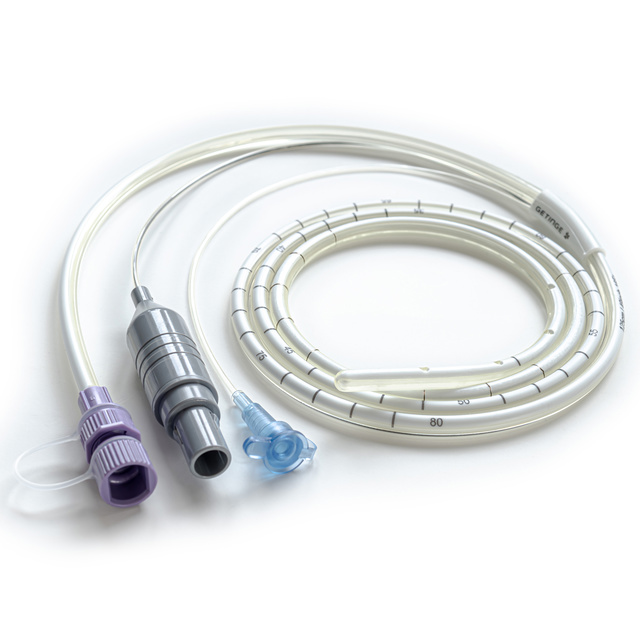
With NAVA, these signals are monitored using micro-electrodes in the Edi catheter which are positioned in the esophagus at the level of the diaphragm. A range of catheters in different French sizes and lengths, ensure optimized signal quality across all patient categories.
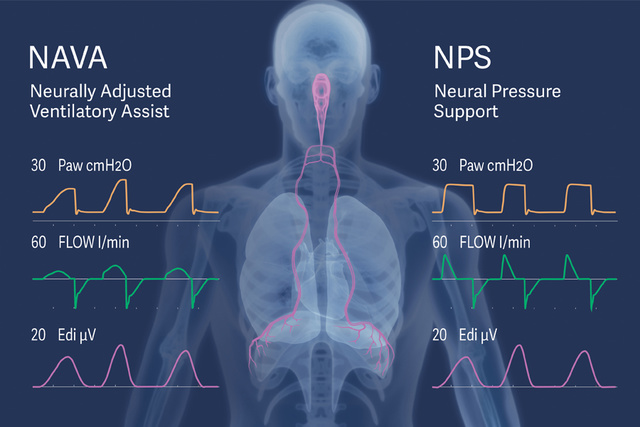
Neural Pressure Support (NPS) and NIV NPS
Neural Pressure Support NPS and NIV NPS is a complement to NAVA and NIV NAVA, delivering time-synchronized pressure support (PS), where both breath triggering and flow termination are based on the patient’s neural respiratory drive. NPS may help reduce the incidence of premature expiratory cycling and harmful eccentric diaphragm contractions, which are common with conventional flow-cycled PS. The faster pressurization rate compared to NAVA may offer advantages in managing restrictive ARDS and obstructive COPD patients.
Innovation
- New 6 Fr / 48 cm size for ELBW neonates
- Usage time prolonged to 7 days
- Shelf life prolonged to 3 years
- Synchronize ventilation with NAVA and NPS
Quality
- Gamma sterilized
- Medical grade polyurethane
- Phthalate and PVC free
- EU MDR 2017/45 certified
Precision
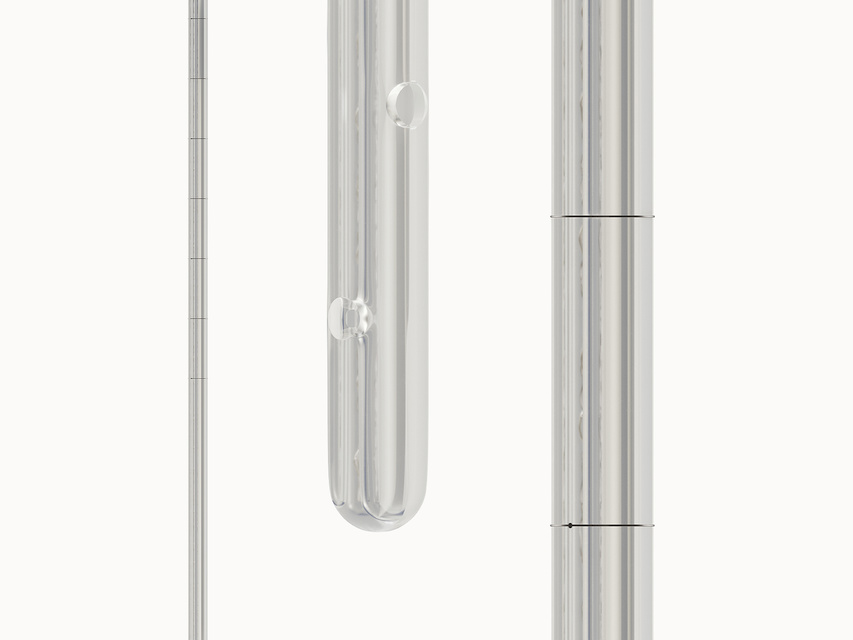
- Number of electrodes: 10
- Inter-electrode distance: 4 - 16 mm
- Insertion distance scale
- X-ray identification Barium sulfate strip
Usability
- Revised neonatal weight ranges
- ENFit enteral feeding connector
- Feeding holes: 2 - 8
- Updated instructions and labeling
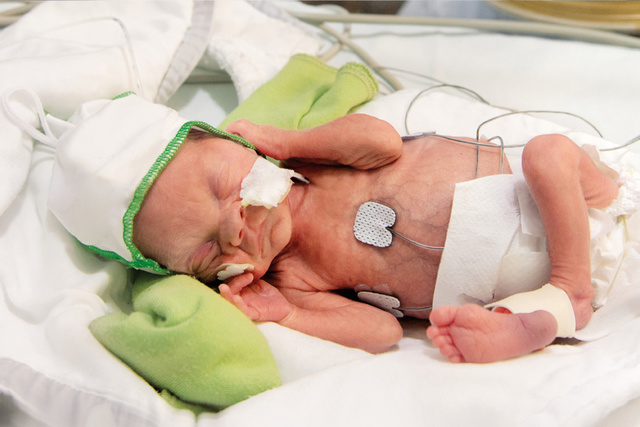
New 6Fr/48 cm size for ELBW neonates
Designed to optimize gastric position of the Edi catheter for extremely low birth weight (ELBW) neonatal patients weighing less than 1000 g, and particularly those in the lower half of the indicated weight range, i.e. 500 - 750 g.

| Name | Patient size | Order number | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Neonatal | 6FR / 48 cm | 0.5–1.0 kg | 68 93 166 |
| 6FR / 49 cm | 0.75–1.5 kg | 68 96 273 | |
| 6FR / 50 cm | 1.25–2.5 kg | 68 93 274 | |
| 8FR / 50 cm | 1.25–2.5 kg | 68 93 275 | |
| Pediatric | 8FR /100 cm | 45–85 cm | 68 93 276 |
| 12FR / 125 cm | 75–160 cm | 68 93 278 | |
| Adult | 8FR / 125 cm | >140 cm | 68 93 277 |
| 16FR / 125 cm | >140 cm | 68 93 279 |
Intended clinical purpose
The Edi catheter ENFit is intended for:
- Administrating nutrition, fluids and medications via the nasogastroenteric or oro-gastroenteric route.
- Aspiration and decompression via the naso-gastroenteric or orogastroenteric route.
- Transfer of electrical activity of the diaphragm (Edi signal) to compatible Servo ventilator
Intended clinical benefits
The clinical benefits with Edi catheter ENFit are:
- To provide monitoring of the patient’s breathing drive. Use of Edi signal to assess and monitor patient-ventilator synchrony and respiratory drive measured in microvolt (μV) per breath.
- To provide medication, hydration and nutrition for patients unable to eat or drink.
Marketing Sales - Sales Flyer
-
The Edi catheter (ENFit) is designed for patients who require continuous monitoring of respiratory drive and patient–ventilator interaction, and is specifically developed for use with the Servo-u and Servo-n ventilators.
Marketing Sales - Brochures
-
Servo-u gives you many options for personalized lung protection and weaning, for treatment of all patient categories. All are easy to understand, implement and use.
-
Servo-n offers an advanced all-in-one solution for personalized lung protection and weaning, helping neonates breathe, sleep and grow.
-
Diaphragm monitoring, helping you improve mechanical ventilation
-
The physiological challenges of mechanical ventilation requires a powerful toolkit, offering the right protection for each patient at the right time.
-
Achieve faster personalized weaning with lung and diaphragm-protective ventilation.
Marketing Sales - Data Sheet
-
Detect electrical activity of diaphragm, with our range of Edi catheters, enabling NAVA and NIV NAVA ventilation modes, and available in all patient categories.
Clinical - Articles
-
Clinical literature, NAVA, NIV NAVA, Edi monitoring, adult patients, meta-analyses, systematic reviews, randomized controlled trials, health economy, detecting asynchrony, monitoring sedation, improving synchrony, improving tidal volume variability lung protective ventilation, gas exchange and hemodynamics, diaphragm protective ventilation, comfort and sleep quality, promoting weaning and extubation, supporting ECMO and ECCO₂R.
-
Clinical literature, nava, niv nava, and Edi monitoring, neonatal, pediatric patients, meta-analyses, systematic reviews,reviews, randomized controlled trials, edi levels, neural breathing pattern, reducing central apneas, reducing sedation needs, improving comfort, improving synchrony, improving oxygenation, reducing inspiratory pressure, improving breathing, variability & hemodynamics, promoting weaning, extubation, supporting adjunctive therapies.
Training Material
-
Flowchart for adult patients, covering NAVA terminology, Edi catheter insertion and positioning, NAVA set-up, workflow, weaning in NAVA and troubleshooting.
-
Flowchart for neonates, including NAVA terminology, Edi catheter insertion and positioning, NAVA set-up, weaning in NAVA and troubleshooting.