Helping patients breathe easier
To support patients suffering from obstructive lung diseases, you can now get our Heliox therapy option on Servo-u, Servo-u MR and Servo-n ventilators. Heliox is a mixture of helium and oxygen that, due to its low density, facilitates laminar flow and minimizes airway pressure. This helps reduce the work of breathing (WoB) of patients with obstructed airways, such as those with asthma or chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD).[1]
*The Servo ventilator and and/or ventilator options presented on this page may be pending regulatory approvals to be marketed in your country. Contact your Getinge representative for more information.
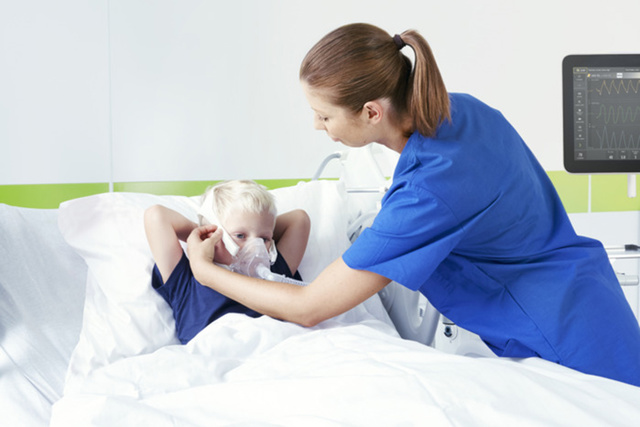

Wide-ranging and safe use
Heliox therapy can be used on a wide range of patients – from infants to adults and for all invasive and noninvasive ventilation modes, as well as in High Flow therapy. In combination with the integrated Aerogen nebulizer, it is often used as an adjuvant treatment while waiting for the onset of conventional pharmacological treatments.
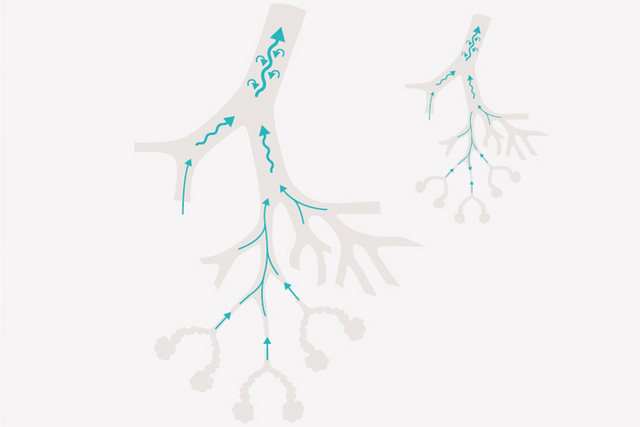
Examples of clinical benefits
Reduction of airway resistance: Heliox reduces air flow resistance within the bronchial tree in patients with obstructive lung disease.[2],[3],[4]
Reduction in the work of breathing: The low density of Heliox improves expiratory flow and decreases resistivework of breathing by converting density dependent turbulent air flow within the airways to laminar flow.[4]
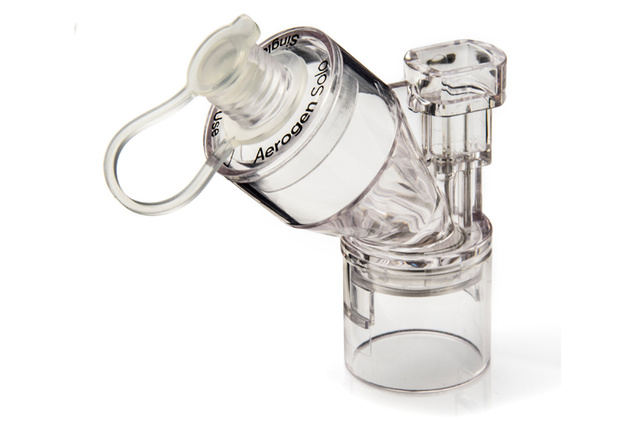

Nebulization and Heliox therapy
Adjunctive therapy for 70 years
Over the past 70 years, Heliox has been used as adjunctive therapy to overcome airflow-obstruction disorders, and been proven to be a safe therapy. Its low density makes it more fluid under conditions or turbulence, promoting a more laminar flow and helping patients to breathe more easily.
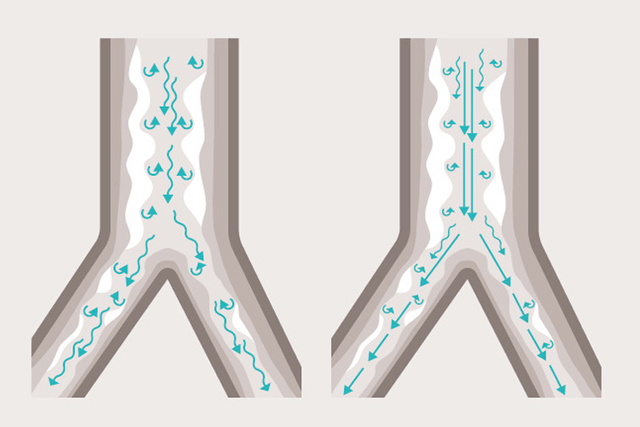
How Heliox therapy promotes better laminar flow with less turbulence
In the illustration above, you can see how the application of Heliox therapy promotes a smoother airflow and easier work of breathing in a typical asthma patient. To the left, note the turbulent air flow that arises in the asthma airway when breathing air/oxygen. By contrast, to the left we see how Heliox improves the laminar flow of breathing, with less turbulence.

New personalized therapy option
The Heliox option can be integrated into your Servo ventilators to provide you with even more therapy options for more personalized ventilation. You can quickly and easily switch between air and Heliox during ventilation without going to standby, saving time and improving comfort for the patient.

Safe, reliable and easy to use
When switching gas from air and O2 to Heliox and back, volume and CO2 monitoring as well as flow delivery are adjusted automatically by the ventilator’s Automatic Gas Identification. Heliox delivery is confirmed by the presence of the "HeO2" symbol on the screen. O2 concentration is easily adjusted between 21% - 100% and information texts facilitate Heliox administration in every mode.

Cost-efficient approach
Your ability to wean patients with more options will support a better clinical result. In addition, the low gas consumption of Servo ventilators makes Heliox therapy cost effective to use. The Heliox therapy, can be added to your Servo-u, Servo-u MR or Servo-n ventilators. However, please note that Heliox therapy is not available in the neonatal patient category.

Key benefits of Heliox with Servo
- Minimizes airway resistance due to laminar flow
- Cost-efficient due to low gas consumption
- Can be combined with all ventilation modes, from invasive to NIV, High Flow therapy and nebulization
- Quick and easy to switch from Heliox to air and back during ventilation
- Adjustable O2 concentration, 21% – 100%